Video • Cell signals
Wound healing: more complex than you think
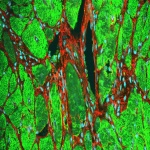
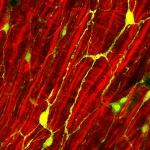
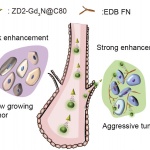
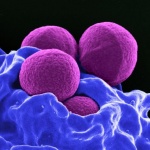
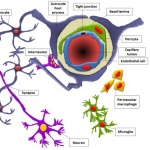
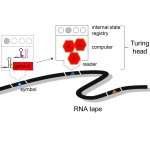
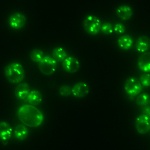
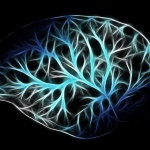
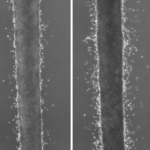
In a sharp and pointy world, wound healing is a critical and marvelous process. Despite a tremendous amount of scientific study, many outstanding mysteries still surround the way in which cells in living tissue respond to and repair physical damage. One prominent mystery is exactly how wound-healing is triggered: A better understanding of this process is essential for developing new and improved…