News • Methylation of microRNA
Is it cancer? New method could tell the difference
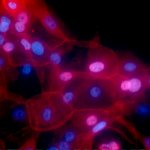
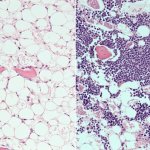
Levels of molecules associated with genetic function, such as microRNA, can be an important indicator of abnormal activity associated with cancer. However, little is known about how different molecules are altered in cancerous cells. Now, researchers from Japan have found a new way of distinguishing cancerous from non-cancerous tissues. In a study published in Nature Communications, researchers…