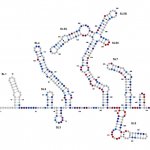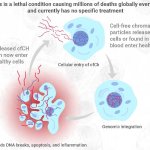
News • Measuring mitochondrial DNA
Rapid blood test identifies Covid-19 patients at high risk of severe disease
One of the most vexing aspects of the Covid-19 pandemic is doctors’ inability to predict which newly hospitalized patients will go on to develop severe disease, including complications that require the insertion of a breathing tube, kidney dialysis or other intensive care. Knowledge of a patient’s age and underlying medical conditions can help predict such outcomes, but there are still…