Article • Predictive biomarkers
Immunotherapy follow-up with MRI: the search is on
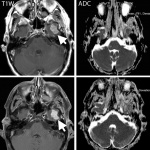
Immunotherapy is taking center stage in imaging, but patient follow-up with CT is no cookie and may fall short in the peripheral limbs, brain and bone marrow. MRI offers specific benefits in these situations, and, combined with PET, it may bring even more results. Research must be carried out on quantitative techniques and tracers developed to fully exploit that potential, Prof. Dow-Mu Koh…