News • Omitting axillary lymph node removal
Breast cancer trial explores benefits of less extensive surgery
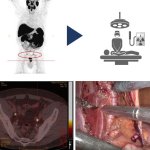
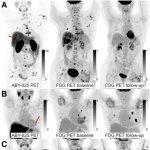
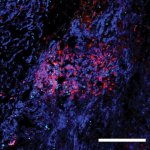
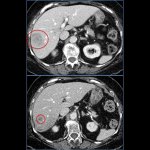
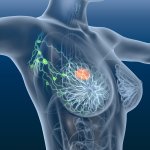
A new trial could pave the way for more gentle surgery of breast cancer: The researchers explore the possibility of sparing the lymph nodes in the armpit - even if metastases are already present.