News • Diagnosis done quick
New sensor tells apart Covid-19 and flu infections - in 10 seconds
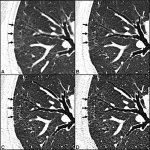
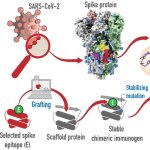
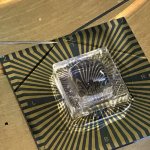
US scientists report using a single-atom-thick nanomaterial to simultaneously detect Covid-19 and flu viruses — at much lower levels and much more quickly than conventional tests for either.