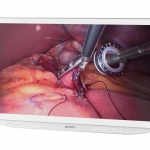
Sponsored • Out goes pixellation
Refining the depth of field for greater surgical precision
John Herman, European Marketing Manager of Sony Healthcare Solutions, explains the potential of 3-D and 4K technologies in medicine.

John Herman, European Marketing Manager of Sony Healthcare Solutions, explains the potential of 3-D and 4K technologies in medicine.
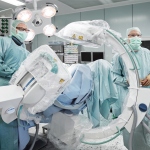
3D imaging is continuously improving, with devices simultaneously becoming more manageable and mobile. The new C-arm system Ziehm Vision RFD 3D is opening up a new dimension. The device was tested by Dr Jan-Sven Jarvers, orthopaedic and trauma surgery specialist at the University Hospital Leipzig, and was introduced last September during the Eurospine Congress in Copenhagen. ‘In the future,…
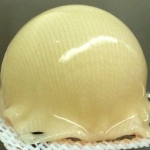
With a goal of treating worn, arthritic hips without extensive surgery to replace them, scientists have programmed stem cells to grow new cartilage on a 3-D template shaped like the ball of a hip joint. What’s more, using gene therapy, they have activated the new cartilage to release anti-inflammatory molecules to fend off a return of arthritis. The technique was demonstrated in a collaborative…
Preliminary tests have demonstrated that a new device may enable existing breast cancer imagers to provide up to six times better contrast of tumors in the breast, while maintaining the same or better image quality and halving the radiation dose to patients. The advance is made possible by a new device developed for 3D imaging of the breast by researchers at the Department of Energy's Thomas…

Doctors and scientists at Intermountain Medical Center in Salt Lake City printed and used a 3D kidney to help save a patient's organ during a complicated tumor-removal procedural. The 3D-printed model allowed doctors to study the patient's kidney in 3D to determine how to best remove the tumor as it was located in a precarious location adjacent to vital arteries and veins. Thanks to the model of…
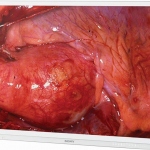
Sony Medical offers an end-to-end video processing chain for medical-grade 4K surgical visualisation. The conversion will not happen overnight, but 4K is a natural next step for improving visualisation during surgery, according to John Herman, the European Marketing Manager for Surgical Solutions at Sony Medical.

During many and various 2015 medical congresses 3-D visualisation has been a key topic as the industry continues to introduce improved hardware and software in ever-shorter intervals. Interventional medicine is entering a new dimension, was a popular slogan. The crystal clear, coloured visualisation of body cavities previously only visible in cloudy black and white may be fascinating, but it does…
In addition the technique to grow the blood vessels in a 3D scaffold cuts down on the risk of transplant rejection because it uses cells from the patient. It was developed by researchers from the University of Bath's Department of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, working with colleagues at Bristol Heart Institute.

To make a good framework for filling in missing bone, mix at least 30 percent pulverized natural bone with some special man-made plastic and create the needed shape with a 3D printer. That’s the recipe for success reported by researchers at The Johns Hopkins University.
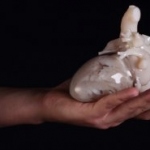
The Materialise Mimics Care Suite is an open and flexible platform that includes planning and design software tools, 3D printed anatomical models and surgical guides, and patient-specific implants. Launched during AAOS, the American Association of Orthopaedic Surgeon’s Annual Meeting, the Suite also introduces Materialise Mimics inPrint, a new software solution that enables surgeons to create…
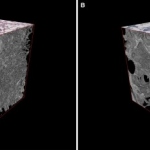
Doctors and scientists at the University of Southampton have used advanced 3D X-ray imaging technology to give new insight into the way an aggressive form of lung disease develops in the body.
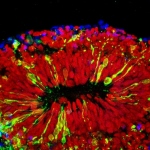
Studying a new type of pinhead-size, lab-grown brain made with technology first suggested by three high school students, Johns Hopkins researchers have confirmed a key way in which Zika virus causes microcephaly and other damage in fetal brains: by infecting specialized stem cells that build its outer layer, the cortex.
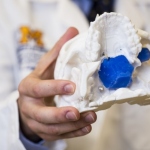
What started as a stuffy-nose and mild cold symptoms for 15-year-old Parker Turchan led to a far more serious diagnosis: a rare type of tumor in his nose and sinuses that extended through his skull near his brain. “He had always been a healthy kid, so we never imagined he had a tumor,” said Parker’s father, Karl. “We didn’t even know you could get a tumor in the back of your nose.”
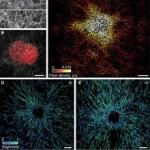
Imaging research is one step closer to giving clinicians a way to do high-resolution scans of malignant cells in order to diagnose cancer and help identify useful therapies. If this technology were to prove successful in clinical studies, it might change how anatomic pathologists and radiologists diagnose and treat cancer.
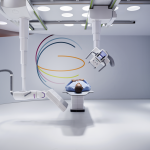
Not all innovations marketed as ‘world premieres’ actually make a significant impact on the world. However, the new robotic X-ray system ‘Multitom Rax’ (Robotic Advanced X-ray) introduced by Siemens Healthcare and the University Hospital Erlangen is one innovation in the world of medicine technology that deserves this label, the manufacturer reports. ‘With the combination of robotic and…

Carestream Health has filed a 510(k) application with the FDA for clearance of its CARESTREAM OnSight 3D Extremity System that uses cone beam CT (CBCT) technology to capture weight-bearing and other types of patient extremity images. This affordable system is designed to offer high-quality, low-dose 3D imaging for use by orthopaedic and sports medicine practices, hospitals, imaging centers,…
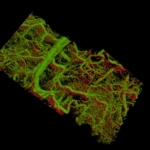
Scientists have many tools at their disposal for looking at preserved tissue under a microscope in incredible detail, or peering into the living body at lower resolution. What they haven't had is a way to do both: create a three-dimensional real-time image of individual cells or even molecules in a living animal.

Identifying a blood disorder may be as easy as running a blood sample from a finger prick under a smartphone. That is the concept behind a new biomedical device being developed by Kansas State University researchers.

Tomosynthesis is an advanced application that allows a multi-slice acquisition and provides a reconstruction of a volume. Several acquisitions at low dose are acquired with a single sweep of the X-Ray tube around the region of interest.
Last year, the DMS Group acquired 100% of the capital of AXS Medical, a French start-up specialized in developing diagnostic tools used for spinal pathologies.
A pioneer in cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) imaging, NewTom recently introduced the only CBCT system with an open gantry and supine positioning, which the firm reports is ‘…ideal for a host of diagnostic needs. Exceeding the limits posed by CT systems, the NewTom 5G XL combines high diagnostic resolution with minimum patient exposure.’

Results from recent trials are promising: an almost 40% increased breast cancer detection rate from digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) screening compared to conventional mammography.
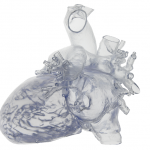
The CSI Congress (Congenital, Structural and Valvular Interventions) is one of the major fixtures for catheter therapy of congenital and structural heart defects. Key moments in this high profile event are live broadcasts and the audience can not only to listen to but also interact with the teams in the cath labs involved.

Taking clear pictures of megaenzymes isn’t easy. But it’s definitely worth it. These proteins play an active role in creating many common antibiotics. They are in constant motion, with sections that flip around acrobatically to carry out necessary tasks. Now, for the first time, McGill researchers have been able to take a series of 3D images of a large section from one of these…

HUS Medical Imaging Center, based in Helsinki, Finland, is undertaking the first European clinical test study of the new CARESTREAM OnSight 3D Extremity System in pre- and post-operative cases. The study of the new cone beam CT (CBCT) scanner and image reconstruction technology, applied within orthopaedic imaging, will last six months and will yield valuable data for both HUS and Carestream…