Sponsored • Radiology equipment
Latest technology meets solid technology
In radiology, it is important to place patients safely and precisely. This works with the "GetUp®" holding system from Febromed.

In radiology, it is important to place patients safely and precisely. This works with the "GetUp®" holding system from Febromed.

When a patient suffers a stroke, speed in treatment can mean the difference between successful recovery, permanent disability, or death. For Christopher Hess, success in stroke diagnosis is a question of workflow and efficient care delivery.
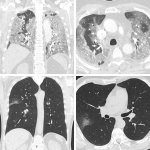
Radiologists in Paris have developed a standardised simple visual lung damage CT severity score for Covid-19 patients who do not have symptoms of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) at the time of initial treatment.
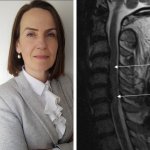
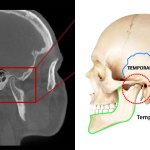
At the BIR virtual congress, spinal imaging specialist Professor Elizabeth Dick focused on approaches and protocols for a range of spinal injuries and discussed assessment and imaging strategies, choice of modalities, and other key factors.
For the Siemens Healthineers team developing new and ever higher performing computed tomographs is daily fare. But when they introduced their most recent CT system an unusual sense of pride was palpable. The photon-counting detector in the new Naeotom Alpha scanner is different from previous models and achieves a level of detail hitherto unknown.
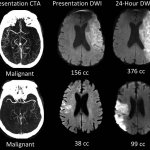
A commonly available imaging technique can identify stroke patients most likely to benefit from a procedure to restore blood flow, a potential breakthrough in care that could save thousands of lives every year

Post-mortem CT (PMCT) increasingly supports pathologists, radiologists and forensic investigators particularly in cases of gunshot fatalities, mass casualties, decomposed and concealed bodies, fire deaths, diving deaths, non-accidental injury cases, and road traffic deaths, in which CT can indicate a pattern of injuries. In Dublin this August, the post-mortem (autopsy) technique was discussed…
Researchers at the Skolkovo Institute of Science and Technology (Skoltech) led by Professor Dylov and their colleagues from First Pavlov State Medical University of St. Petersburg, Russia, have developed a brand-new approach to the task of 3D image segmentation — figuring out the contours of the constituent parts in a complex structure. While their so-called negative volume segmentation…

The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) cleared the first new major technological improvement for Computed Tomography (CT) imaging in nearly a decade. “Computed tomography is an important medical imaging tool that can aid in diagnosing disease, trauma or abnormality; planning and guiding interventional or therapeutic procedures; and monitoring the effectiveness of certain therapies,” said…
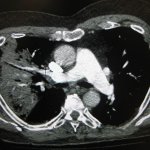
Unsupervised deep learning breaks new ground by predicting the progression of COVID-19 and survival of patients directly from their chest CT images.
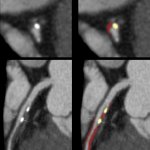
Coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) is a non-invasive imaging test which can be used to evaluate coronary artery stenosis and measure plaques. Current plaque analysis is time-consuming and needs expert readers in order to help assess a patient’s heart attack risk. That’s about to change.

An AI-led device to assess coronary CT angiographs has been designed to assess cardiac plaque that may lead to myocardial infarction (MI). In his presentation ‘Vascular inflammation and cardiovascular risk assessment using coronary CT angiography’ (CCTA), Charambalos Antoniades, Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine at the University of Oxford, presented the research team’s findings during…
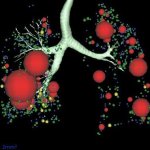
A novel CT scan-based approach has revealed significant changes in a parameter indicating lung destruction in some asthmatics. This finding could lead to more personalized treatments for asthma accompanied by persistent airflow limitation. Clinicians have long thought that some people with asthma experience declines in their lung function, called fixed airflow obstruction (FAO), due to changes to…

At a virtual European event, Fujifilm Healthcare Europe presented a complete and integrated portfolio of diagnostic products and services, including CT, MRI, X-ray, AI, PACS, endoscopy and ultrasound systems. This launch follows the completion of Fujifilm's acquisition and takeover of Hitachi's Diagnostic Imaging-related business on 31 March 2021 for 179 billion yen (€1.3 billion).

‘Accutron CT-D Vision is the latest evolution of Medtron`s flagship CT injector. Designed to enhance operability, the updated user interface is displayed on larger touch screens and provides a simplified programming and more comprehensive follow-up of each injection step,’ the company reports. ‘The new IDS (Injection Data Sharing) option enables injection data to be shared through RIS/PACS…
With the launch of the Accutron CT-D Vision, MEDTRON AG once again demonstrates their status as a partner to radiologists. Focusing on the operator's needs, the latest evolution of the Accutron CT-D enhances the usability of its double head CT injector and optimizes its integration into the radiology environment.

A new project for radiation exposure reduction aims to improve justification of computed tomography (CT) in Europe through co-ordinated action. For this, the European Society of Radiology has been awarded the European Commission Tender ‘European co-ordinated action on improving justification of computed tomography’ (acronym: EU-JUST-CT). The project started on 7 April 2021 and will last until…

CT scanning used to uncover remnants of malignancy hidden inside medieval bones provides new insight into cancer prevalence in a pre-industrial world. The first study to use x-rays and CT scans to detect evidence of cancer among the skeletal remains of a pre-industrial population suggests that between 9-14% of adults in medieval Britain had the disease at the time of their death. This puts cancer…

Dunlee announces that it has successfully installed its first CT replacement tubes with liquid metal bearing (LMB): the new DA200P40+LMB tube with Dunlee CoolGlide technology. Prior to this first installations, the DA200P40+LMB tube with Dunlee CoolGlide technology was rigorously tested at both Dunlee's facility and on independent external gantries to confirm that it will perform reliably in both…
Febromed GmbH & Co. KG, the expert in delivery room equipment and medical accessories from Oelde, Germany, has developed “get up”, an innovative handle system for radiology.
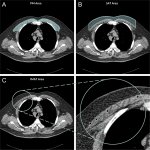
Body composition information derived from routine chest CTs can provide important information on the overall health of people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), including their risk of all-cause mortality. This is the result of a new study, published in Radiology. COPD is a group of chronic, progressive lung diseases that affect about 30 million people in the United States alone.…

Liquid metal bearing (LMB) technology has been a key aspect of extending the lifespan of CT scanners, improving workflow, and enhancing patient and operator experience via noise reduction. The LMB concept has been pioneered by Dunlee, with senior CT product manager Robert Bayerlein noting that the Hamburg-based company has a long heritage in imaging innovation.
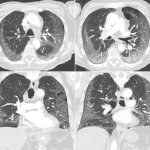
The results of a large-scale study indicate that the introduction of an AI-powered solution by healthcare software company Radlogics into radiology workflow to analyze Chest-CT scans during the Covid-19 pandemic reduced report turnaround time by an average of 30 percent, which is equivalent to 7 minutes per case.
Improving workflow is one of the major challenges that radiology departments face. The need to be more efficient, deliver timely and effective patient care, and keep an eye on costs are all factors that seem to be ever-present in the modern imaging department. With the added demands of the coronavirus pandemic as radiology departments continue to play a critical role in the fight against…

With public health issues continuing to make daily mainstream news headlines across the world, it is clear how much change the healthcare environment is going through. Not only are there existing pressures on resources, space, staff, certain procedures, and budgets, but there are brand new ones resulting from the ongoing global COVID-19 pandemic. This has led to an even greater need for…