© DFKI GmbH
News • Image-based diagnosis of Covid-19
AI detects coronavirus on CT scans
In order to detect the Corona virus SARS-CoV-2, there are further methods of diagnosis apart from the globally used PCR tests (Polymerase chain reaction): The infection can also be recognised on CT scans – for which Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be used as well.
An AI system can not only filter CT scan of Covid-19 patients from a data set, but also estimate, which areas of the image are of interest. In a new research project, Prof. Dr.-Ing. Daniel Sonntag, head of the research department Interactive Machine Learning (IML) of the German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI), and scientist Duy Nguyen have developed a new prototype for the automatic recognition of SARS-CoV-2 infections on CT scans in cooperation with researchers from Dublin City University (Ireland), University of California, Berkeley (USA), VNUHCM-University of Science (Vietnam) and Max Planck Institute for Informatics.
Recommended article
Interview • Chest X-ray, CT and more
Imaging the coronavirus disease COVID-19
Chest X-ray is the first imaging method to diagnose COVID-19 coronavirus infection in Spain, but in the light of new evidence this may change soon, according to Milagros Martí de Gracia, Vice President of the Spanish Society of Radiology (SERAM) and head of the emergency radiology unit at La Paz Hospital in Madrid, one of the hot spots for viral re-production of COVID-19.
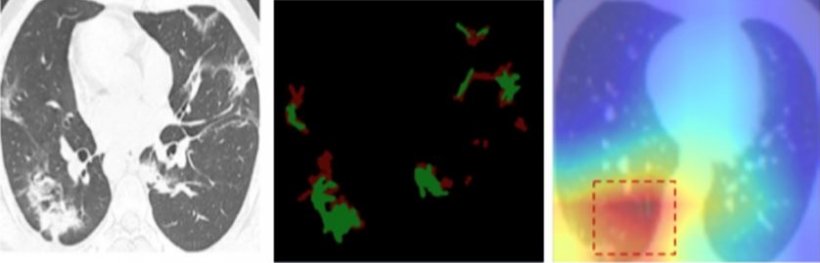
In a joint paper, of which Mr. Duy Nguyen is the lead author and which was presented in the “Trustworthy AI for Healthcare” workshop of the 35th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, the researchers present a method to improve the diagnosis and decrease errors by combining different data sources. In a test run with research data, the method achieved a success rate of 92 percent – according to the most recent status, this is the worldwide best result in automated image recognition of infections with SARS-CoV-2 on a CT scan data set. A noteworthy aspect of the method is that, in order to assist medical staff, it visually marks the area on which the diagnosis is based.
The image depicted above shows the CT scan of a lung (left) that is analysed via the method of automated image recognition. In addition, patients can be examined for acute or chronic illnesses by using so-called ground glass opacity (GGO). The AI system eventually marks the area upon which its decision is based on a so-called heatmap (right). This visual explanation of the assisting system aims at making the diagnosis more comprehensible and giving further insights to doctors and medical staff: The automatic image recognition with high precision helps estimating the infection and planning the treatment. Especially when shortages in medical supply are possible, this decision aid can be an important advantage.
Source: German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence (DFKI)
04.02.2021