News • Neuroscience & Alzheimer's disease
Researchers identifiy subset of neurons that are most susceptible to Alzheimer's disease
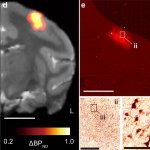
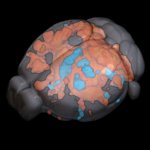
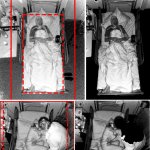
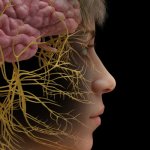
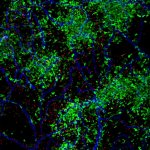
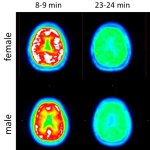
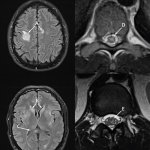
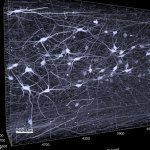
Neurodegeneration, or the gradual loss of neuron function, is one of the key features of Alzheimer's disease. However, it doesn't affect all parts of the brain equally.