News • Neuronal disorder
Tracking the onset of ataxias
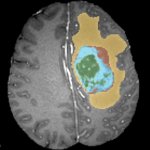
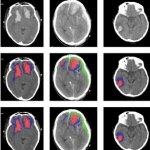
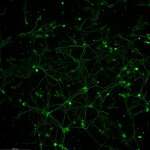
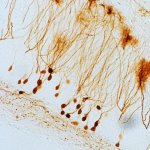
“Spinocerebellar ataxias” are diseases of the nervous system associated with a loss of motor coordination. A European research alliance headed by the German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases (DZNE) and the University of Bonn has now registered whether and how symptoms of ataxia developed over the years in around 250 persons at risk, who initially did not show symptoms. This is the first…