News • Dangerous fever
Febrile convulsions: an early indicator for epilepsy in children?
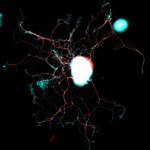
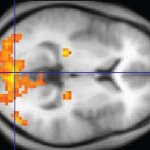
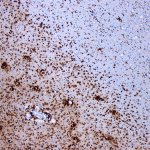
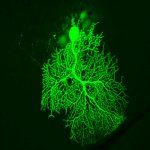
Children who suffer repeated febrile convulsions have an increased risk of developing epilepsy and psychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia and depression later in life. This is shown by a comprehensive register-based study from Aarhus University. The risk of febrile convulsions increases with the child’s fever, and approximately four per cent of Danish children suffer from febrile…