News • 3D microelectrodes
Promising approach for pain relief without side effects
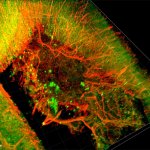
Researchers at Lund University in Sweden have developed a completely new stimulation method, using ultra-thin microelectrodes, to combat severe pain. This provides effective and personalised pain relief without the common side effects from pain relief drugs. The study, which was conducted on rats, has been published in the research journal Science Advances.