News • Natural system
Papillomaviruses promote skin cancer
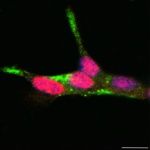
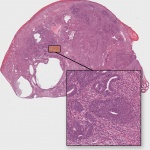
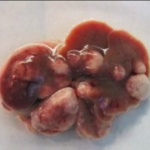
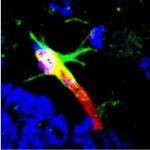
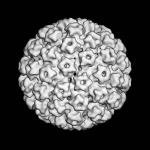
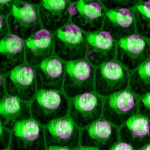
UV radiation has been known for a long time to be a risk factor for the development of skin cancer. Simultaneous infection with human papillomaviruses (HPV) has also been suspected to promote skin cancer, particularly in organ transplant recipients. Scientists from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) have now been able to show for the first time in a natural system that papillomaviruses…