News • Promising preclinical study results
Epilepsy: Gene therapy shows long-term suppression of seizures
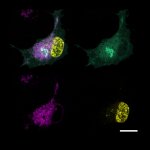
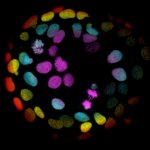
Teams of researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the Medical University of Innsbruck have developed a new therapeutic concept for the treatment of temporal lobe epilepsy. It represents a gene therapy capable of suppressing seizures at their site of origin on demand. Having been shown to be effective in an animal model, the new method will now be optimized for clinical use.…