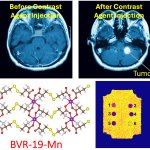
News • Manganese MOF nanoparticles
New material to make MRI contrast agents greener, safer, sharper
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) serve as the basis for a novel type of MRI contrast agent, which the developers hope can outperform current agents while being less toxic for the patient.