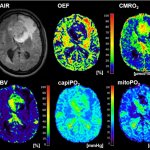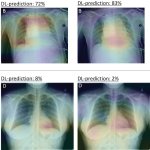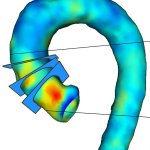
News • Evaluation of high- and low dose therapy regimens
Knee osteoarthritis: Every bit of exercise helps, but...
Both high and low dose exercise therapy have beneficial effects in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. However, a new Swedish study shows that, sometime, more can indeed be more.