News • Oncology
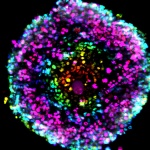
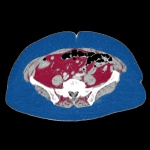
Breaking through a tumor's defenses
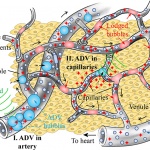
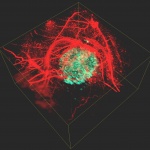
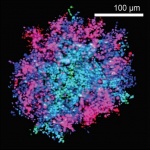
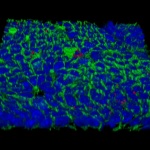
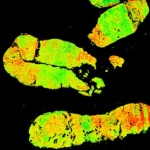
Babraham Institute researchers have shown that some tumours use not one but two levels of protection against the immune system. Knocking out one level boosted the protective effects of the second and vice versa. The research demonstrates that a two-pronged approach targeting both cell types simultaneously may offer a promising route for the development of new cancer immunotherapies.