Article • Tissue analysis
Infrared spectroscopy as a diagnostic tool
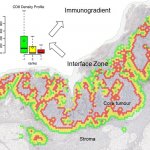
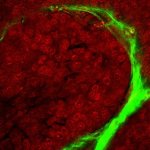
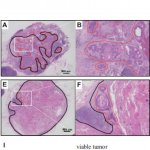
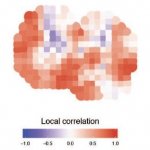
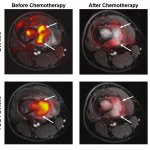
New techniques of infrared-based technology are showing strong potential for cost-effective tissue analysis. Peter Gardner, Professor of Analytical and Biomedical Spectroscopy at the University of Manchester, outlined how hyperspectral imaging coupled with sophisticated computer algorithms can identify and grade cancerous tissue, as well as offer an indication of prognosis. The technique, he…