News • Immune system
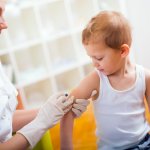
Tuberculosis vaccine also makes less susceptible to other infections
A tuberculosis vaccine developed 100 years ago also makes vaccinated persons less susceptible to other infections. While this effect has been recognized for a long time, it is not known what causes it. Together with colleagues from Australia and Denmark, researchers from Radboud university medical center the universities of Nijmegen and Bonn have now presented a possible answer to this question.