News • Promising alternative to heart transplants
'Artificial aorta' to reduce blood pressure
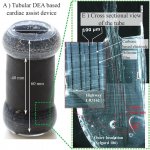
Engineers at EPFL’s Center for Artificial Muscles have developed a silicone aorta that can reduce how hard patients’ hearts have to pump. Their breakthrough could offer a promising alternative to heart transplants. “Over 23 million people around the world suffer from heart failure. The disease is usually treated with a transplant, but because donated hearts are hard to come by, there is an…