News • Researchers look into mammoplasty aftereffects
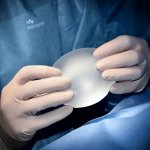
Immune system disorders after silicone breast implant surgery
Russian scientists have conducted a comprehensive examination of why some women present with autoimmune conditions after silicone augmentation mammoplasty.