
A new definition for plastic surgery
Gathering in Austria, plastic surgeons proclaim the need for clarification and standards. Michael Krassnitzer reports

Gathering in Austria, plastic surgeons proclaim the need for clarification and standards. Michael Krassnitzer reports

New research carried out in the UK has revealed that young children with congenital heart disease are at risk of having harmful toxins in their blood, particularly following surgery. Mark Nicholls reports

‘We are all aware of the importance of early diagnosis and rapid appropriate treatment of patients with severe sepsis. Yet, many patients still do not receive satisfactory early management and the application of recent guidelines for sepsis management is still inadequate,’ writes Jean-Louis Vincent MD PhD, from the Intensive Care Department, Erasme Hospital, Université Libre de Bruxelles,…
Xenon anaesthesia not only preserves the heart and circulation but also prevents post-operative delirium. The high cost of the gas is made up for by a shorter length of sta. Report: Holger Zorn

Point of care technologies (POCT) have an important, quality enhancing, risk-reducing and cost-impacting role within the extremely time-critical medical decision structures of a central Accident and Emergency department, says Professor Wilfried von Eiff, Centre for Hospital Management, University of Muenster, Germany.
France – Re-opening clogged arteries with metal stents has proved a life-saver for a majority of patients with coronary disease. Yet the high rates of complications and mortality for patients with diabetes following a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) continue to baffle cardiologists. Report: John Brosky

Medication errors sit among the top ten causes of harm to patients. They can, of course, occur in any department, but it’s still a surprise that they happen as frequently in anaesthetics departments, considering anaesthetists’ expertise is in handling tricky medication. However, apparently they are not the fault of the professional, but of the nature of the processes. Report: Karoline…
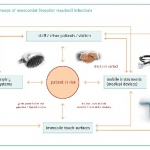
In Europe, nosocomial infections cause about 25,000 deaths every year. Copper has strong antibiotic effects and may reduce hospital acquired infections.
Bacteria are highly flexible when it comes to choosing a vehicle to enter a human body. During orthopaedic surgery, they may well settle on a prosthetic joint and cause immediate or delayed infections.
In late May, a particularly aggressive and new strain of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) posed an enormous challenge for northern German hospitals. In Hamburg, the focus of the epidemic, more than 1,000 people fell ill, about 180 of them seriously, after getting into contact with the bacterium. Report: Meike Lerner
United Kingdom – A call has been made for tighter regulatory controls to ensure the safety regulation of medical devices, following joint investigations carried out by the British Medical Journal and the Channel 4 TV programme Dispatches, which were televised and published online at BMJ.com this May.

One year ago interventional cardiologists raised champagne glasses to celebrate the first publication of clinical evidence showing that transcatheter valve implants (TAVI) is safe and effective. In May at EuroPCR 2011, cardiologists raised magnifying glasses to look closer at further clinical results. John Brosky reports from Paris

Bypass surgery figures declined again in 2010. Reason: Most coronary heart disease (CHD) patients are being treated by removal of the obstruction followed by stent implantation -- a situation criticised by Professor Jochen Cremer, first Vice President of the DGTHG (German Society for Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery).
The UK -- Patients admitted to hospital with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) face a six-fold greater risk of death if they become infected with Clostridium difficile, according to a new study carried out by researchers at Imperial College London and St George’s Healthcare NHS Trust (pub: Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics).

Initially meant to bridge the gap before a heart transplant is performed, today ventricular assist devices (VADs) are increasingly considered ‘a lasting therapy option’, according to Professor Heinrich Schima, Head of the Centre for Medical Physics and Biomedical Technology at the Medical University of Vienna.
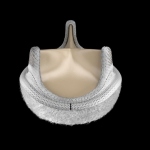
Edwards Lifesciences Corporation, a global leader in the science of heart valves and hemodynamic monitoring, announced that interim data from a multi-center European prospective study of the investigational EDWARDS INTUITY Valve System showed promising results for patients undergoing surgical aortic valve replacement (AVR).

Major disasters and natural catastrophes occur all the time – but in most cases we are only aware of them as images in the news on our TV screens or in the newspapers. Fortunately, most European hospitals are confronted with such major events only occasionally.

It turns out to be difficult to find out exactly how much a child who cannot yet speak suffers after a surgical operation. Researchers at the University Hospital of La Paz, in Madrid, have validated the 'Llanto' scale, the first, and only, tool in Spanish which measures infant pain rapidly and simply.

This March, Heinz-Dieter Hilgers arrived for his once-monthly check-up at Ruhrlandklinik in Essen. Last June, his situation was far less relaxed. Suffering chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) for almost two years, he had been listed for a lung transplant since April 2009. During his wait for an organ, his illness increased.
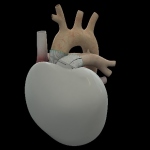
A little over three decades after the world's first human heart transplant (HT), Carmat’s life-size artificial heart, a mix of animal tissue, titanium and missile technology that perfectly replicate a human heart, might save the lives of thousands.

Neurocardiology – especially atrial fibrillation (AF) – was the key topic during a press conference held during the 55th Annual Congress of the Germany Society for Clinical Neurophysiology and Functional Imaging (DGKN) this March. For good reason: Worldwide, there are around six million AF sufferers -- and it is one of the most common causes of stroke because this cardiac irregularity can…

Over 8,000 international clinicians and scientists travelled to Berlin in March to attend the International Liver Congress 2011, hosted by The European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), to hear the latest research, perspectives and treatments in hepatology.
The critical care expertise available before a severely injured person can be admitted to hospital is “incomplete, unpredictable, and inconsistent,” shows research published online in Emergency Medicine Journal. Ambulance services are often reliant on volunteer doctors with variable levels of expertise and the availability of specialist doctors is patchy, particularly over evenings or…

During intensive care, hyperglycaemia and insulin resistance are widespread in diabetics as well as non-diabetics. However, whether the normalisation of blood glucose levels with insulin therapy improves the prognosis of such patients is still debated. Karoline Laarmann reports
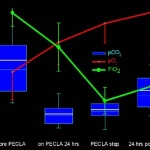
Often a life-saving intervention, mechanical ventilation also has some serious drawbacks: the need for sedation, the risk of ventilator associated pneumonia, intubation or tracheostomy related complications. In 1972, Donald Hill from Pacific Medical Centre, Los Angeles, reported the first successful long-term mechanical lung assist device with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).