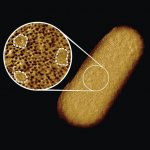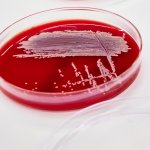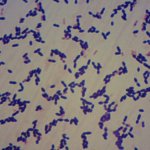
News • Streptococcus pneumoniae
Technique helps discover whether bacteria are antibiotic resistant
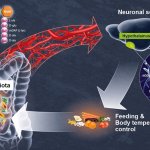
A new study could one day help health workers determine whether bacteria of the species Streptococcus pneumoniae, which cause meningitis, are resistant to antibiotics.