News • Fighting antibacterial resistance
Continued COVID levels of hygiene could transform infection control
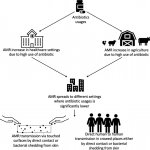
Making recommendations for change, academics analyzed global data into the prevalence of antimicrobial resistance in urban areas—the rise of which is threatening the lifesaving role of the medications.