Sponsored • All in one scan
World's First Total-Body PET/CT with 194 cm Axial FOV installed in Europe
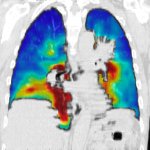
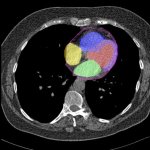
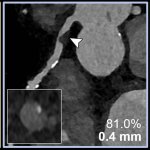
The IRCCS in Bologna has inaugurated a state-of-the-art integrated PET/CT system. This cutting-edge technology allows for the entire human body to be studied in a single scan, even detecting the smallest tumour cells.