Image source: Hologic
Article • Digital breast tomosynthesis
Transforming breast screening: The role of AI in improving reading workflow
Breast cancer screening recommendations in the European Union have changed dramatically in the past year, with a focus on the use of more advanced imaging technology. In 2022, the European Council updated the Article 168 recommendations to encourage the widespread adoption of digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) for all breast cancer screenings.
Author: Dr. Stephanie Sauer, Head of Womens Imaging Department, Institute of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University Hospital Würzburg

Image source: University Hospital Würzburg
The decision to endorse DBT by both the European Commission Initiative on Breast Cancer and the European Council will facilitate greater access to DBT for women across Europe. DBT has been shown to detect up to 65% more invasive cancers than a 2D mammogram alone,1 and can reduce false positive rates compared to full field digital mammography.2
While having more centers adopt DBT into their practice is a positive change, it also presents some challenges for radiologists—particularly the increased number of images for radiologists to review. This challenge has paved the way for AI to offer innovative workflow solutions for radiologists that do not sacrifice accuracy.
Utilizing AI to support reading workflow
As more health centers in Europe look to adopt DBT technology, efficiency and optimized workflow will be more critical than ever for radiologists interpreting DBT images. The 3D gantries capture thousands of detailed 1mm images, which means that the increased volume of images can extend radiologists' reading time and reduce efficiency.
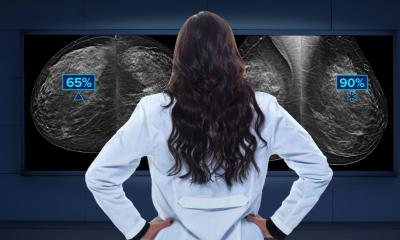
AI tools have revolutionized this workflow by offering rapid and precise analysis of breast screening datasets. During image acquisition, AI software provides key metrics that allow the radiologists to categorize and prioritize cases by complexity. Beyond this, by leveraging advanced analytics, AI tools can reconstruct data from DBT exams to produce overlapping 6mm slices, ensuring there is no loss of 3D image data and maintaining continuity in scrolling.3,4 These slices speed up reading time by reducing the number of images to review, with no compromise in image quality, sensitivity or accuracy.5 As a result, radiologists can streamline their workflow and expedite patient care, translating to potential time savings. When reading these layered slices, which reduce the number of 3D images to review by 2/3 compared to 1mm slices3, radiologists experience an average time savings of 1 hour per day, based on eight hours of interpretation time.4
Additionally, AI tools that create these 6mm slices can reduce data storage space and network traffic. Since DBT generates additional images compared to 2D mammograms, the large file sizes require adequate Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) storage and high network bandwidth. By utilizing AI workflow tools that generate slices, an approximate file size reduction of 60% in the DBT dataset can be achieved due to the smaller number of final slices.6 This can enable a quicker load time to help radiologists review images more easily.
Image source: Hologic
Adopting DBT for patient care
DBT is essential for early breast cancer detection. Findings from the Tomosynthesis plus Synthesized Mammography (TOSYMA) study found that DBT plus synthesized mammography detected 3.5 times more invasive cancers than digital mammography alone in the first screening round.7 These results show the impact DBT has on screening accuracy as it instills confidence in women and their radiologists during routine mammograms.
Not all DBT systems are equal though, and the European Reference Organisation for Quality Assured Breast Screening and Diagnostic Services (EUREF) highlights best examples of quality control in mammography screening from regional and national breast cancer programs across Europe. To date, the only DBT system to successfully pass its stringent Type Test is Hologic’s 3Dimensions mammography system. As health centers explore adopting DBT systems, administrators should review quality standards like EUREF to ensure they are purchasing a gantry that helps facilitate improved patient care. Additionally, these systems should not only be compatible with today’s AI solutions but also have the capabilities to adapt to those technologies in the future.
The incorporation of AI tools into mammography reading workflow has enabled radiologists to save valuable time while maintaining the highest standards of accuracy. By utilizing tools like 3D image slices, radiologists can effectively manage the growing volume of images, and still deliver precise interpretations for timely and accurate diagnoses. It also frees up space for improved data storage to facilitate better PACS reading.
With the European Council’s recognition of DBT as the premier mammography technology, the need for integration of AI in breast cancer screening workflows is given. As DBT becomes more widely available, AI paves the way for more efficient health care practices.

References:
- Results from Friedewald, SM, et al. “Breast cancer screening using tomosynthesis in combination with digital mammography.” JAMA 311.24 (2014): 2499-2507; a multi-site (13), non-randomized, historical control study of 454,000 screening mammograms investigating the initial impact the introduction of the Hologic Selenia® Dimensions® on screening outcomes. Individual results may vary. The study found an average 41% increase and that 1.2 (95% CI: 0.8-1.6) additional invasive breast cancers per 1,000 screening exams were found in women receiving combined 2D FFDM and 3D™ mammograms acquired with the Hologic 3D Mammography™ System versus women receiving 2D FFDM mammograms only.
- Destounis, S. V., Morgan, R., & Arieno, A. Screening for dense breasts: Digital Breast Tomosynthesis. American Journal of Roentgenology, 2015; 204(2), 261–264.
- Tech File: TFL-00059
- Report: CSR-00116
- Sauer ST, Christner SA, Kuhl PJ, Kunz AS, Huflage H, Luetkens KS, Schlaiß T, Bley TA, Grunz JP. Artificial-intelligence-enhanced synthetic thick slabs versus standard slices in digital breast tomosynthesis. Br J Radiol. 2023 Apr 1;96(1145):20220967. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20220967. Epub 2023 Apr 17. PMID: 36972100; PMCID: PMC10161903.
- Hologic file: WP-00152-EUR-EN
- Weigel et al.: Breast Density and Breast Cancer Screening with Digital Breast Tomosynthesis: A TOSYMA Trial Subanalysis; Radiology 2023
11.12.2023
- AI (824)
- breast cancer (626)
- digitisation (95)
- imaging (1640)
- mammography (258)
- radiology (730)
- screening (218)
- tomosynthesis (8)
- women's health (338)
- workflow (495)