Sponsored • Beyond average
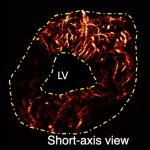
A technological solution for preventing device-detected subclinical AF?
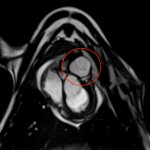
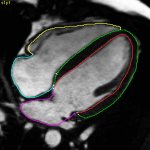
As pharmacological options for subclinical Atrial Fibrillation and atrial high-rate episodes continue to run into challenges, new research suggests more physiological pacing solutions can help reduce risks of progression to clinical AF.