News • Leukemia MRD after chemo
AML: Residual cancer testing as an important safeguard
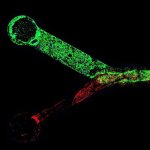
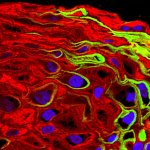
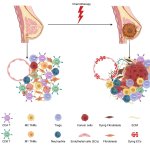
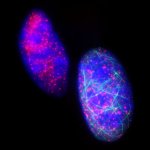
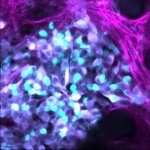
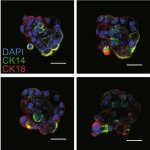
Blood cancer cells can remain in the blood of AML patients, even after chemotherapy seemed successful. Testing for these residuals before blood cell donation is a vital precaution, a new study finds.