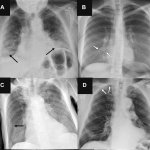
News • Chest X-ray evaluation
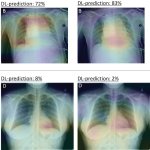
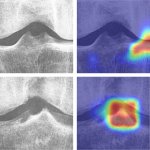
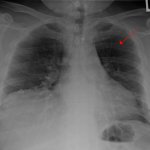
Human readers still outperform AI in lung disease identification
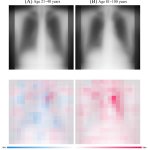
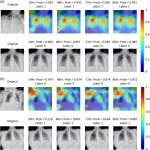
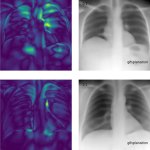
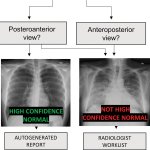
Reports of AI gaining the upper hand in diagnostic imaging interpretation are piling up, but there are still areas where the eye of a trained human radiologist remains superior.