News • Flexible electronics and human stem cells
‘Biohybrid’ device could restore function in paralysed limbs
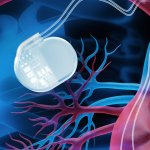
Cambridge researchers have developed a new type of neural implant that could restore limb function to amputees and others who have lost the use of their arms or legs.