News • Mapping the 'family tree' of cancer
Metastasis monitoring: CRISPR tool catches cancer 'in the act'
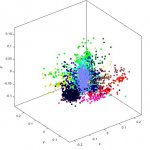
When cancer is confined to one spot in the body, doctors can often treat it with surgery or other therapies. Much of the mortality associated with cancer, however, is due to its tendency to metastasize, sending out seeds of itself that may take root throughout the body. The exact moment of metastasis is fleeting, lost in the millions of divisions that take place in a tumor. “These events are…