News • Here comes the tooth fairy
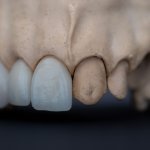
New drug shows promise for regenerating lost teeth
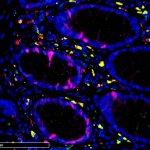
A new study by scientists at Kyoto University and the University of Fukui may offer hope for adults who have lost their teeth. The team reports that an antibody for one gene - uterine sensitization associated gene-1 or USAG-1 - can stimulate tooth growth in mice suffering from tooth agenesis, a congenital condition. The paper was published in Science Advances. Although the normal adult mouth has…