
News • Longevity
One for all: Convergent mechanism of ageing discovered
Researchers have discovered folate metabolism as a fundamental process for ageing. This could provide a new opportunity to improve human health during ageing on a broad basis.

Researchers have discovered folate metabolism as a fundamental process for ageing. This could provide a new opportunity to improve human health during ageing on a broad basis.

Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory have published the first detailed atomic-level model of the SARS-CoV-2 "envelope" protein bound to a human protein essential for maintaining the lining of the lungs.

A new project led by University of California San Diego Biological Sciences graduate student Joshua Borin has provided evidence that phages that undergo special evolutionary training increase their capacity to subdue bacteria.
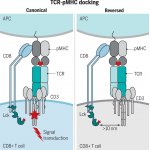
Monash University researchers have provided a fundamental advance regarding how T cells become activated when encountering pathogens such as viruses.
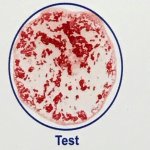
A team of Johns Hopkins researchers has developed a rapid blood test that could confirm a person has been vaccinated while they wait to board a plane or enter a sporting event.

Researchers have shown that the life expectancy of mices can be increased by an average of 30% in both males and females. For humans, that would means that a 90-year-old could live until nearly 120.
Months after recovering from mild cases of COVID-19, people still have immune cells in their body pumping out antibodies against the virus that causes COVID-19, according to a study from researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. Such cells could persist for a lifetime, churning out antibodies all the while.

Understanding every step in the life cycle of a virus is crucial for identifying potential targets for treatment. Now, scientists at the Institute of Science and Technology (IST) Austria were able to show how a virus from the retrovirus family – the same family as HIV – protects its genetic information and becomes infectious. Furthermore, they show an unexpected flexibility of the virus. This…
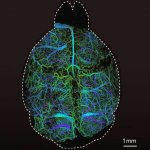
Researchers from ETH Zurich and University of Zurich have developed a new microscopy technique that lights up the brain with high resolution imagery. This allows neuroscientists to study brain functions and ailments more closely and non-invasively.
Switching off a heart muscle protein could provide a new way for drugs to combat heart failure in people who’ve had a heart attack, according to research led by the University of Cambridge and published in the journal Nature. There is an unmet need to find drugs that can successfully improve the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently after it’s been damaged following a heart attack.…

Two clusters of brain cells compete to promote either the persistence or disappearance of traumatic memories, according to a new study conducted in mice. The findings could provide important insights into human conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and associated problems such as alcohol use disorder (AUD) that can arise from the persistence of traumatic…
A new idea for treating Alzheimer’s disease could eradicate the toxic proteins most closely linked to cognitive decline in the places where they do the most damage, a study from researchers at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons suggests. The study was published online in Science Translational Medicine.
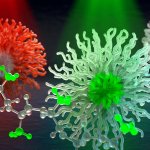
Before the huge potential of tiny nanocarriers for highly targeted drug delivery and environmental clean-up can be realized, scientists first need to be able to see them. Currently researchers have to rely on attaching fluorescent dyes or heavy metals to label parts of organic nanocarrier structures for investigation, often changing them in the process. A new technique using chemically-sensitive…

A study of healthcare workers shows they were three times more likely to become infected during the Covid-19 pandemic compared to the general population. Around one in five of workers who were infected were asymptomatic and unaware they had Covid-19. The study published in ERJ Open Research also shows that it was not only frontline staff who faced the higher risk, suggesting that there was…
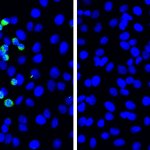
Scientists from Hokkaido University have discovered a novel defensive response to SARS-CoV-2 that involves the viral pattern recognition receptor RIG-I. Upregulating expression of this protein could strengthen the immune response in COPD patients.
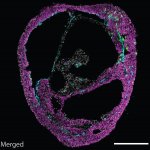
Self-organizing heart organoids – developed at the Austrian Academy of Sciences – are also effective injury- and in vitro congenital disease models. These “cardioids” may revolutionize research into cardiovascular disorders and malformations of the heart. The results are published in the journal Cell.

Almost 1 million extra deaths relating to the Covid-19 pandemic occurred in 29 high income countries in 2020, finds a study published by The BMJ. Except for Norway, Denmark and New Zealand, all other countries examined had more deaths than expected in 2020, particularly in men. The five countries with the highest absolute number of excess deaths were the US, UK, Italy, Spain, and Poland.
Researchers from Case Western Reserve University have identified a potential new approach to better controlling epilepsy. Lin Mei, professor and chair of the Department of Neurosciences at Case Western Reserve School of Medicine, who led the new study in mouse models, said the team found a new chemical reaction that could help control epileptic seizures.
University of Birmingham scientists have developed a new microscopic imaging approach to take a closer look at 3D-printing for developing future patient implants, as well as improved disease modelling and drug screening. Additive manufacturing (3D printing) platforms create bioprinted structures by moving a special bioink, containing cells, biomolecules and materials, through a narrow tube, but…

Thin-film electrodes developed at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) have been used in human patients at the University of California, San Francisco, generating never-before-seen recordings of brain activity in the hippocampus, a region responsible for memory and other cognitive functions. In a study published in the journal Nature Communications, surgeons at UCSF placed the flexible…
Using higher doses of antibiotics in a bid to tackle the growing problem of drug resistance may end up strengthening certain bacteria, according to research that highlights a previously unthought-of risk.

Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have developed a new material that prevents infections in wounds – a specially designed hydrogel, that works against all types of bacteria, including antibiotic-resistant ones. The new material offers great hope for combating a growing global problem. The World Health Organization describes antibiotic-resistant bacteria as one of…

Antibiotic resistant bacteria are a looming super threat – heralding a time when our drugs will no longer be effective against prevalent infections. Hospitals are already coping with treatment-resistant bacterial infections. Cognizant of the threat and thinking outside the box, BGU scientists and German and American colleagues have developed a pair of 'molecular tweezers' to destroy the biofilm…
When a cell is infected, SARS-CoV-2 not only causes the host cell to produce new virus particles. The virus also suppresses host cell defence mechanisms. The virus protein nsP3 plays a central role in this. Using structural analyses, researchers at Goethe University in cooperation with the Swiss Paul Scherrer Institute have now discovered that a decomposition product of the virostatic agent…
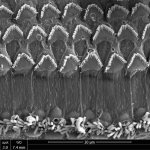
A gene called GAS2 plays a key role in normal hearing, and its absence causes severe hearing loss, according to a study led by researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. The researchers, whose findings are published online in Developmental Cell, discovered that the protein encoded by GAS2 is crucial for maintaining the structural stiffness of support cells…