Image source: NUS
News • RNA editing
New mechanism of cancer formation discovered
A team of scientists at the National University of Singapore (NUS) led by Dr Polly Leilei Chen from the Cancer Science Institute of Singapore and Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine has discovered a previously unknown mechanism of cancer formation, the understanding of which may lead to more effective treatment.
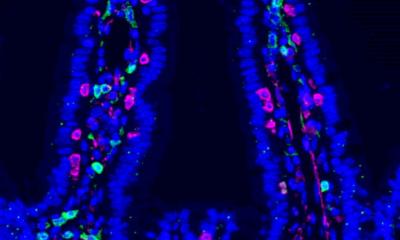
Their findings concern a process called RNA editing. The DNA code of a gene gets transcribed into an intermediate code known as RNA, before being translated into a protein molecule that plays a particular role in the cell. Sometimes, the RNA gets modified, or edited, before the final translation, yielding a different protein product. RNA editing is a phenomenon that gives the cell finer control over its proteins.
With this new knowledge, we can now look into how A-to-I RNA editing contributes to cancer by altering their protein sequences and how we can restore cancer-suppressing processes mediated by RNA editing in the cell
Polly Leilei Chen
The research team examined the RNA encoding a protein called “coatomer subunit α” (COPA), which influences the development of cancers of the liver, esophagus, stomach and breast, and examined whether RNA transcribed from the COPA gene was edited or altered in clinical samples of cancerous liver tissues. They discovered that any given cell contains a mix of both edited and unedited versions of COPA. When the unedited or “wild type” COPA is predominant, the cell is more likely to become cancerous. Conversely, when edited COPA is predominant, it is thought to suppress a convoluted molecular signalling network called the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling pathway. When this pathway gets out of control, it triggers excessive cell multiplication which can lead to cancer.
The researchers are now trying to find a way to boost the natural RNA editing mechanisms in the cancerous cell to tip the balance in favour of the edited version of COPA, thereby suppressing the cancer. “With this new knowledge, we can now look into how A-to-I RNA editing contributes to cancer by altering their protein sequences and how we can restore cancer-suppressing processes mediated by RNA editing in the cell,” said Dr Chen.
Source: National University of Singapore
16.01.2021