News • Bacteria
New discovery could change ICU care
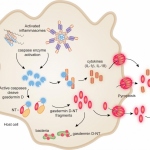
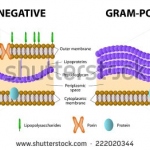
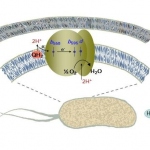
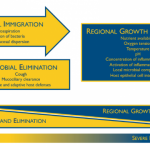
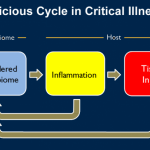
No one knows for sure how they got there. But the discovery that bacteria that normally live in the gut can be detected in the lungs of critically ill people and animals could mean a lot for intensive care patients.