News • Prevalence prediction
COVID-19 will probably become seasonal, but...
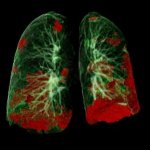
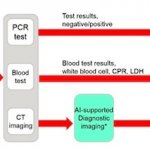
Researchers predict that COVID-19 will likely become seasonal, waning in the summer and prevalent in the winter. But, only once herd immunity is achieved through natural infection or vaccinations. Until then, COVID-19 will be here year-round.