News • Neuroscience
A deep dive into the brain
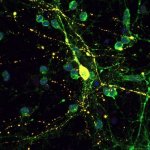
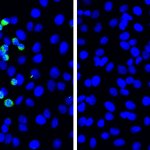
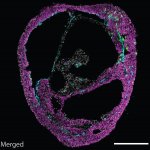
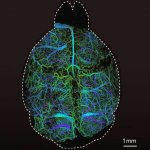
Researchers from ETH Zurich and University of Zurich have developed a new microscopy technique that lights up the brain with high resolution imagery. This allows neuroscientists to study brain functions and ailments more closely and non-invasively.