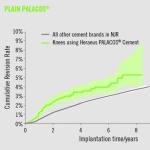
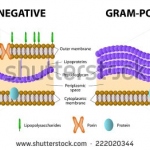
Interview • Multiresistant pathogens
'Antibiotics don’t generate large profits'
During our European Hospital interview with specialist in microbiology, virology and infection epidemiology Beniam Ghebremedhin MD, from the University Hospital Wuppertal, spoke about the impact of migration on infections, and ways to tackle the problem of multiresistant pathogens. ‘There is a lack of specialists in infectious diseases, for direct patient care on hospital wards as well as in…