News • Pathogenic microbes
Cigarette smoke makes MRSA superbug bacterium more drug-resistant
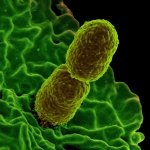
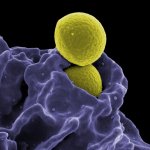
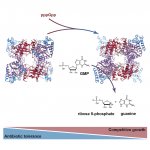
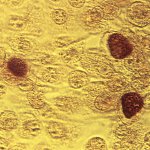
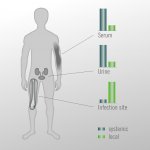
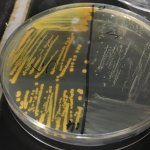
Cigarette smoke can make MRSA bacterial strains more resistant to antibiotics, new research from the University of Bath has shown. In addition cigarette smoke exposure can make some strains of Staphylococcus aureus – a microbe present in 30-60% of the global population and responsible for many diseases, some fatal – more invasive and persistent, although the effect is not universal across all…