Article • Antibiotic stewardship
Screening with multiplexed kits
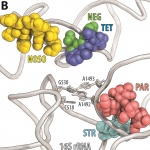
Antibiotic stewardship is becoming a critical concern in hospitals as antibiotic resistance spreads globally and some organisms become resistant to antibiotics of last resort. Molecular diagnostics can play a role in antibiotic stewardship programs by providing timely and accurate advice to clinicians on which antibiotics to use, Professor Keith Stanley advises. "Antibiotic resistance in the…