Article • Men are from Mars, women are from Venus
Sex differences in imaging cardiovascular disease
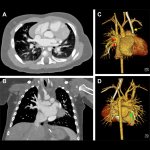
An interplanetary title for a quite down-to-earth topic: The symposium "Men are from Mars, women are from Venus" at the EACVI congress (European Association of Cardiovascular imaging) launched into the differences between the hearts of men and women. While the speakers could firmly establish that both sexes share the same home world, variations in their cardiac anatomy warrant a more…