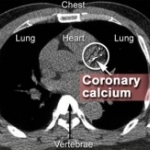
Arterieal calcium scan predicts death risk
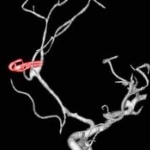
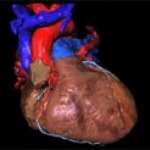
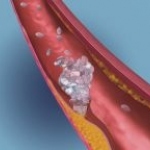
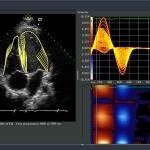
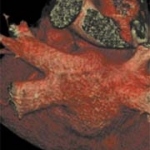
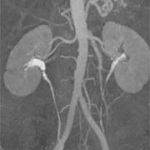
Scanning the heart's arteries for calcium deposits might be one of the best ways to predict the overall risk of death for adults with cardiac trouble, a new study suggests. This might also help end the controversial discussions about calcium scans.