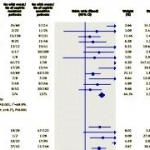
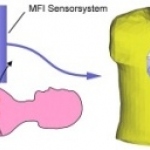
Cardiovascular molecular imaging - is it ready for internal medicine diagnostics?
Imaging in Internal Medicine is among the main topics for 114th Congress of the German Society of Internal Medicine (March. Wiesbaden). Specialists in internal medicine, radiologists, and nuclear medicine have developed a programme that will not only provide an overview of the values of modern imaging procedures but also tackle controversial subjects.