Article • Infection control
Knowledge is one thing - implementation another
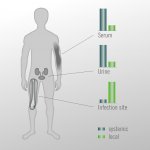
Insufficient knowledge of infection control, resulting in insufficient compliance, increases the risk of hospital acquired infections (HAIs) and multiresistant pathogens that put patients at risk. At the 2019 Annual General Meeting of the German Society for Hygiene and Microbiology e.V. (DGHM) in Göttingen, Professor Frauke Mattner, Senior Consultant at the Institute of Hygiene, Kliniken der…