News • Stem cell research
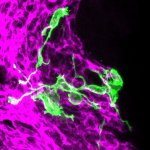
Brain confetti - why our sense of smell declines when we get old
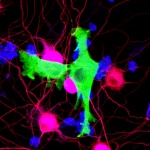
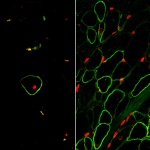
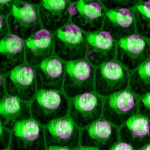
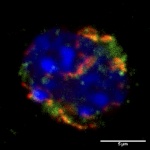
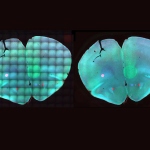
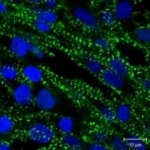
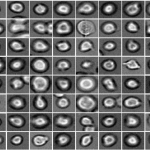
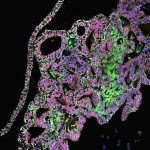
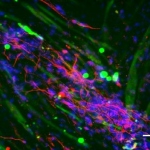
As mammals age, their sense of smell deteriorates. In a study published in the journal ‘Cell Reports’, an interdisciplinary research team at Helmholtz Zentrum München and the University Medical Centre Mainz investigated why this is the case. For their study, the researchers tracked the development of stem cells in the brains of mice using what are known as confetti reporters. They then…