News • Freefrom Reversible Embedding of Suspended Hydrogels
A 'FRESH' way to 3D-print tissues and organs
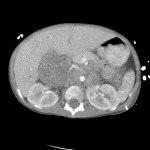
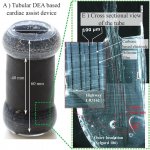
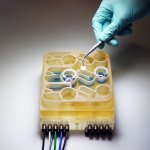
Research into 3D bioprinting has grown rapidly in recent years as scientists seek to re-create the structure and function of complex biological systems from human tissues to entire organs. The most popular 3D printing approach uses a solution of biological material or bioink that is loaded into a syringe pump extruder and deposited in a layer-by-layer fashion to build the 3D object. Gravity,…