Metal attacks norovirus head on
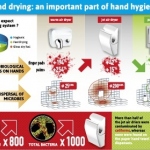
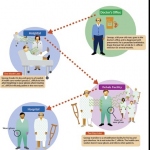
The Norovirus, which affects around 267 million people and is attributed to cause over 200,000 deaths annually (usually among the very young, elderly or immune-suppressed, or in 3rd world areas) can be rapidly destroyed by copper and copper alloys, scientists at the United Kingdom’s University of Southampton confirm.