News • Infection research
Understanding lung damage in Covid-19 patients
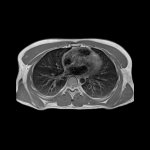
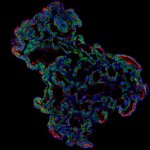
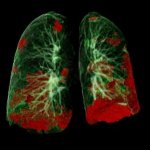
Covid-19 disease severity is determined by the individual patient’s immune response. The precise mechanisms taking place inside the lungs and blood during the early phase of the disease, however, remain unclear. Researchers from Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, the Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) and Freie Universität Berlin have now studied the cellular mechanisms…