News • Vigorous ventilation
Covid-19: Why faster air exchange in buildings is not always beneficial
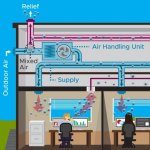
Vigorous and rapid air exchanges might not always be a good thing when it comes to addressing levels of coronavirus particles in a multiroom building, according to a new modeling study. The study suggests that, in a multiroom building, rapid air exchanges can spread the virus rapidly from the source room into other rooms at high concentrations. Particle levels spike in adjacent rooms within 30…